INFORMATION CENTER
How much do you know about positive pressure dust removal systems
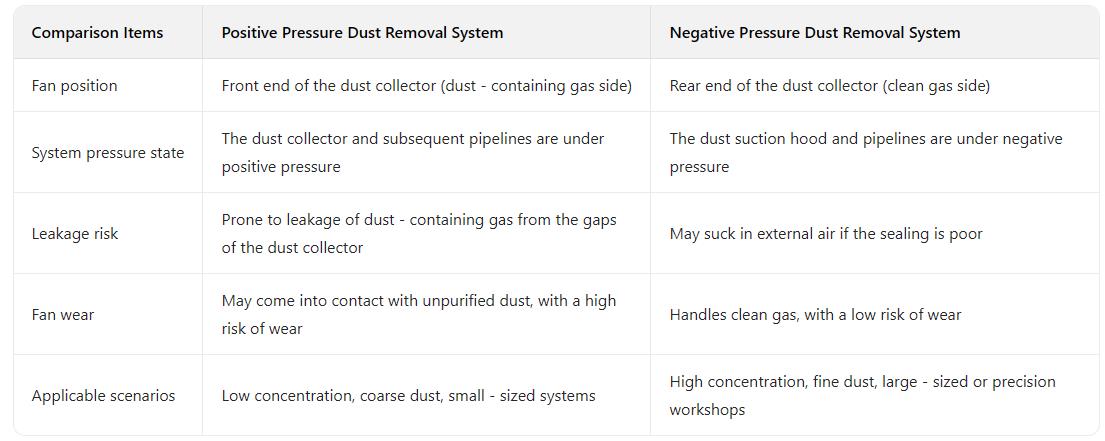
The positive pressure dust removal system is a common form of ventilation and dust removal in the industrial dust removal field. Its core feature is that the fan is located at the front end of the dust removal system (i.e., before the dust - containing gas enters the dust collector). With the power of the fan, the dust - containing gas is "pressed" into the dust collector for purification treatment, and the inside of the system (from the fan to the dust collector and the air outlet) is in a positive pressure state.
1. Basic Composition of Positive Pressure Dust Removal System
A positive pressure dust removal system usually consists of the following key components, and each part works together to complete the whole process of dust collection, transportation, purification and discharge:
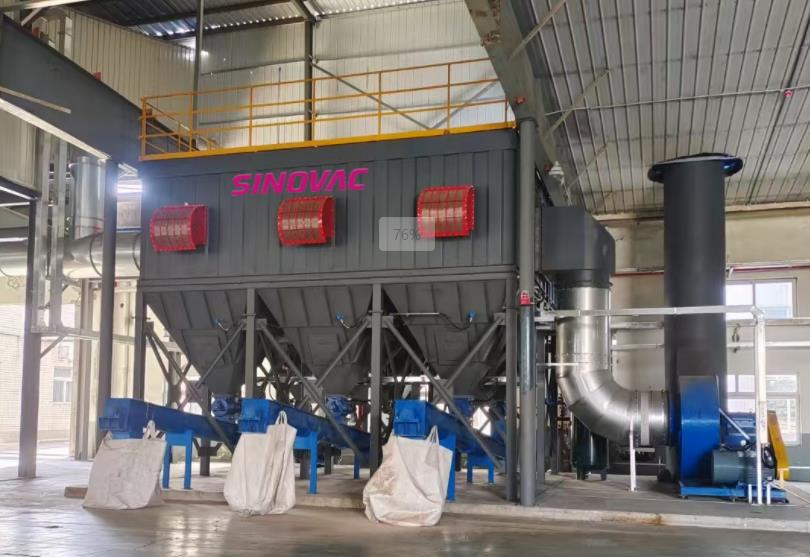

Dust suction hood / dust suction port: Installed at the dust - generating point (such as the dust - raising part of workshop equipment) to capture and collect dust - containing gas.
Pipeline system: Connects the dust suction hood with the fan and the dust collector, and is responsible for transporting the dust - containing gas. The pipeline design should consider the wind speed to avoid dust deposition.
Fan: As the power source, it is located at the front end of the system (between the dust suction hood and the dust collector), and sends the dust - containing gas into the dust collector after pressurization.
Dust collector: The core purification equipment (such as bag filter, cyclone dust collector, etc.), which filters or separates the dust - containing gas sent in under positive pressure to remove dust.
Exhaust device: The clean gas purified by the dust collector is discharged outdoors through the exhaust port (or chimney).
2. Working Principle of Positive Pressure Dust Removal System
Dust collection: The dust generated at the dust - generating point is captured by the dust suction hood, and enters the pipeline under the negative pressure suction of the fan (the local area at the front end of the fan is negative pressure).
Pressurized transportation: After the dust - containing gas is sucked in by the fan, it is pressurized by the impeller to form a positive pressure air flow, which is "pressed" into the dust collector through the pipeline.
Purification treatment: The dust - containing gas is purified in the dust collector by means of filtration, centrifugal separation, etc., and the dust is captured (such as the filter bag of the bag filter intercepts the dust).
Discharge: The purified clean gas is directly discharged from the air outlet of the dust collector (due to the positive pressure of the system, no additional power is needed), and is discharged into the atmosphere or reused after meeting the standards.
3. Advantages and Disadvantages of Positive Pressure Dust Removal System
Advantages:
Relatively simple structure: The fan is located at the front end, and the purified gas is directly discharged. There is no need to set an additional fan or complex pipeline behind the dust collector, which saves equipment cost and installation space.
Convenient fan maintenance: The fan handles unpurified dust - containing gas, but because the fan is at the front end of the positive pressure section, if the design is reasonable (such as matching with pretreatment), it can reduce the direct wear of dust on the fan (compared with the case where the fan in the negative pressure system handles the purified gas, it needs to be judged according to the nature of the dust).
Suitable for specific scenarios: When the dust - generating points are scattered or the clean gas needs to be reused in the workshop (such as maintaining positive pressure in the workshop to prevent external pollution), the positive pressure system is easier to realize.
Disadvantages:
High risk of dust leakage: The inside of the system (dust collector and subsequent pipelines) is in a positive pressure state. If the equipment is not well sealed, the dust - containing gas may leak from the gaps, causing secondary pollution.
High requirements for dust collectors: The dust collector needs to withstand the impact of positive pressure air flow and have good sealing performance; otherwise, it will affect the dust removal efficiency and cause leakage.
Not suitable for high - concentration / fine dust: If handling high - concentration or ultra - fine dust, the unpurified gas directly entering the fan may aggravate the wear of the impeller and shorten the service life of the fan.
4. Applicable Scenarios of Positive Pressure Dust Removal System
Occasions where the dust - generating points are relatively concentrated, the dust concentration is low and the particles are relatively coarse (such as wood processing, grain storage, etc.), which can reduce fan wear.
Scenarios where the workshop environment requirements are not high, or the purified gas needs to be reused (such as drying workshops need to recover heat).
Small - sized dust removal systems: Due to their simple structure and low cost, they are suitable for working conditions with small air volume.
5. Comparison with Negative Pressure Dust Removal System
In practical applications, the type of system needs to be selected according to the nature of the dust, the air volume to be handled, environmental protection requirements, etc. In some scenarios, a "positive pressure + negative pressure" combined system can also be used to optimize the effect.
Contact Us
—
Address: 608, block a, National Convention and Exhibition Center, No. 1998, Zhuguang Road, Qingpu District, Shanghai
Tel: 15121023409 Manager Wang

We provide OEM production for more customers who really understand vacuum cleaning system.
© Shanghai Wellson Environmental Technology Co., Ltd.